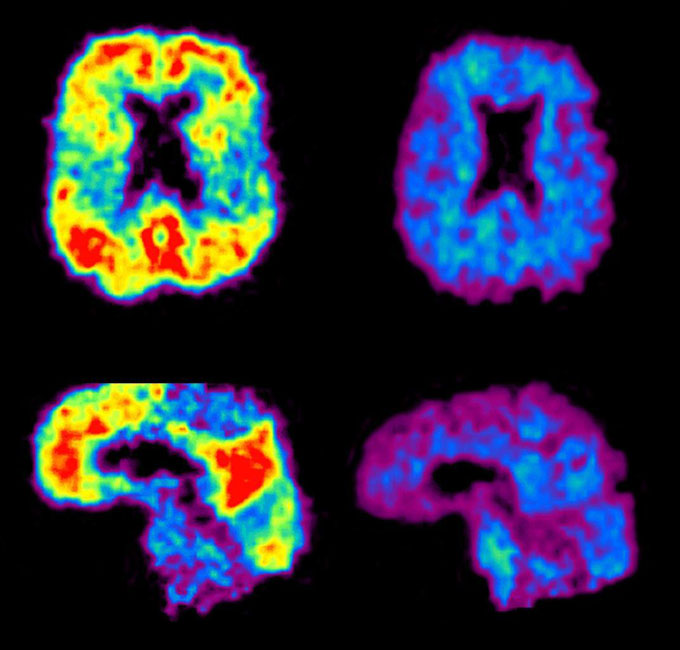
Alzheimer’s disease is hard to diagnose. But proteins in the blood might provide clarity. A series of recent findings, presented at the annual Alzheimer’s Association International Conference in Philadelphia and in research papers, raise the possibility of a simple blood draw to help doctors figure out if a person’s cognitive problems are caused by Alzheimer’s […]
Author: houssem23
A black hole made from pure light is impossible, thanks to quantum physics
Black holes can’t be formed from pure light. Quantum physics would curb their creation under any foreseeable conditions, a new study suggests. Typically, matter is responsible for black holes. They’re often formed when a star’s core implodes at the end of its life. But matter isn’t necessarily required to form a black hole. According to […]
Extraordinary heat waves raise questions about our A/C use
An extraordinary heat wave last week toppled thousands of temperature records across Asia, from Iran to Japan. In Iran’s highlands, the city of Isfahan, at the foothills of the Zagros Mountains, sweltered in temperatures up to 43.8° Celsius (110.8° Fahrenheit). Japan, which saw at least 120 deaths due to heatstroke in July, issued more heat […]
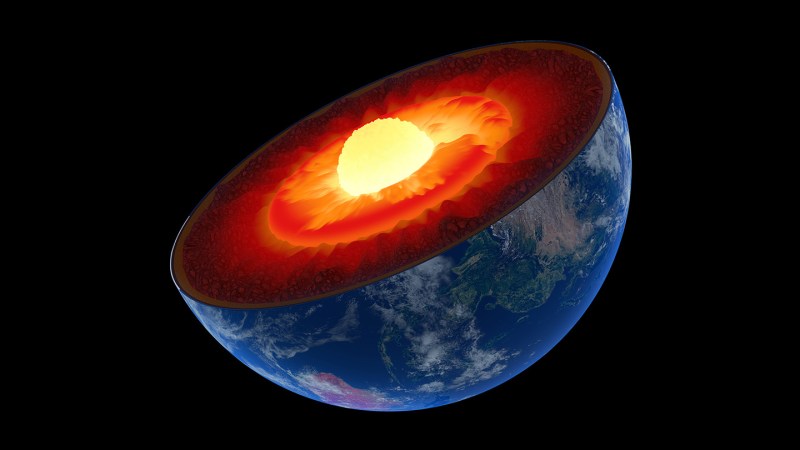
Something weird is happening to Earth’s inner core
Something strange is happening at Earth’s center. Decades of earthquake data show that Earth’s inner core has been rotating slower than its mantle and surface since around 2010, researchers report June 12 in Nature. The study appears to confirm a controversial finding from last year that the inner core may have reversed its rotation relative […]
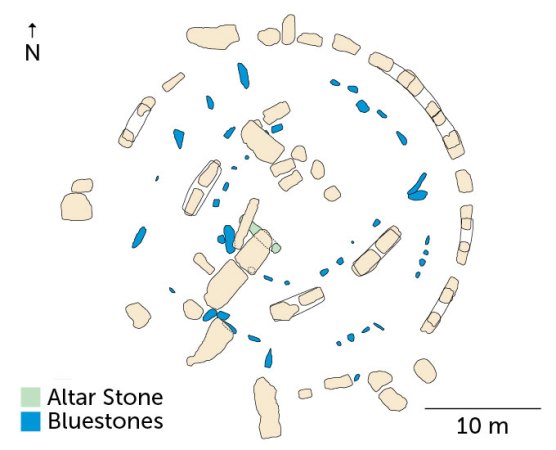
Stonehenge’s mysterious Altar Stone had roots in Scotland
Stonehenge had a hard Scottish heart, a new study suggests. The ancient site’s central stone, a large slab known as the Altar Stone, consists of rock transported at least 750 kilometers from northeastern Scotland to southern England, say geoscientist Anthony Clarke of Curtin University in Perth, Australia, and colleagues. An analysis of the age and […]
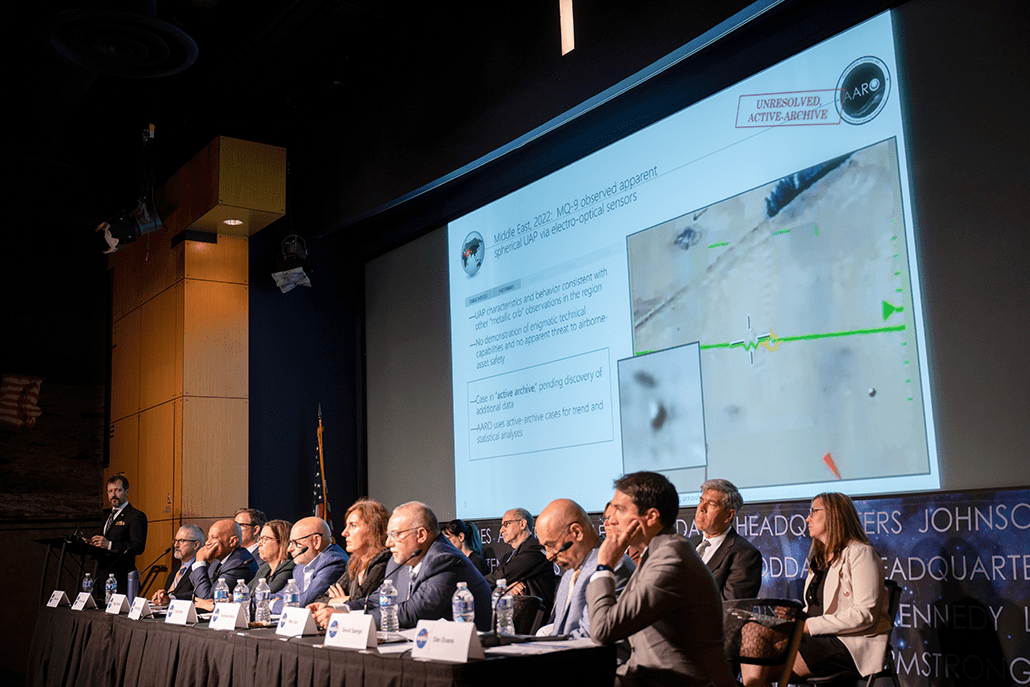
Scientists are getting serious about UFOs. Here’s why
For millennia, humans have seen inexplicable things in the sky. Some have been beautiful, some have been terrifying, and some — like auroras and solar eclipses before they were understood scientifically — have been both. Today’s aircraft, balloons, drones, satellites and more only increase the chances of spotting something confounding overhead. In the United States, […]
4 questions about the uranium needed for next-generation nuclear reactors
Nuclear power of the future is going to need fuel. That has governments, energy companies and nuclear engineers clamoring to get their hands on HALEU: high-assay low-enriched uranium. HALEU (pronounced like “Hey, Lou”) was previously a niche material, used mainly in nuclear reactors conducting scientific research. But now, multiple companies in the United States have […]
The asteroid that may have killed the dinosaurs came from beyond Jupiter
Earth’s most famous killer asteroid came from the outer reaches of the solar system, researchers report in the Aug. 16 Science. About 66 million years ago, an asteroid slammed into the sea just off Mexico’s Yucatán Peninsula, forming the Chicxulub crater. That powerful impact may have triggered a mass extinction event on Earth, killing off […]
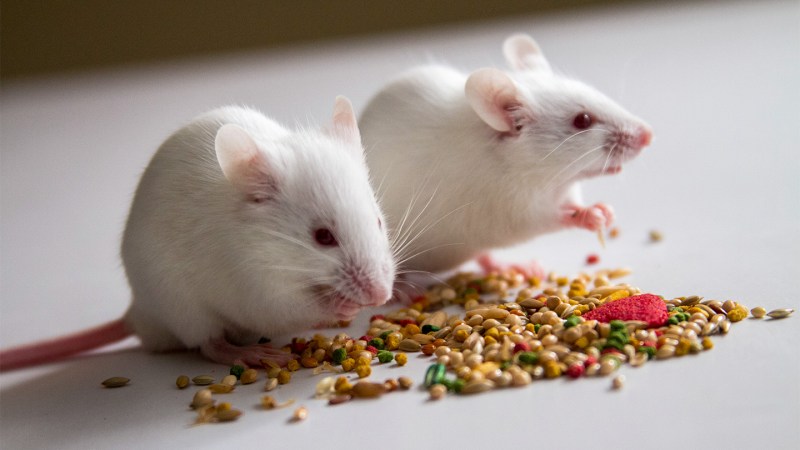
A hunger protein reverses anorexia symptoms in mice
An appetite-stimulating protein can reverse anorexia in mice. Mice with lack of appetite and weight loss — symptoms similar to people with anorexia — that were genetically tweaked to secrete a protein called ACBP ate more food and weighed more than anorexic animals with an ACBP deficit, researchers report August 14 in Science Translational Medicine. […]
Some meteors leave trails lasting up to an hour. Now we may know why
To leave a lasting trail, meteors need to aim low. A new survey of shooting stars shows that meteors that blaze through 90 kilometers up in the sky leave a persistent afterglow, unlike those that burn up at greater heights. Meteors are normally blink-and-you’ll-miss-it events. A particle of space dust leaves a fiery trail of […]